e-Invoicing FAQs
1. Is e-Invoicing mandatory for all businesses in Malaysia?
Yes, e-Invoicing will become mandatory for all businesses, with the implementation dates varying based on the company's annual turnover thresholds as outlined above.
2. How can businesses prepare for e-Invoicing implementation?
Businesses should:
- Assess and upgrade their accounting and invoicing systems to ensure compatibility with e-Invoicing requirements.
- Train staff on new processes and compliance obligations.
- Consult with tax professionals or service providers specialising in e-Invoicing solutions.
3. Are there any exemptions to e-Invoicing requirements?
Certain entities, such as individuals not conducting business and taxpayers with annual turnover below RM150,000, may be exempt. However, it's essential to consult the latest guidelines from the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) for specific exemptions. Check out our comprehensive article for e-Invoicing exemptions in Malaysia.
4. What is the e-Invoicing treatment during the interim relaxation period?
Taxpayers are given a six (6) month interim relaxation period from their date of mandatory implementation. The e-Invoicing interim relaxation period is applicable to all phases of e-Invoice implementation.
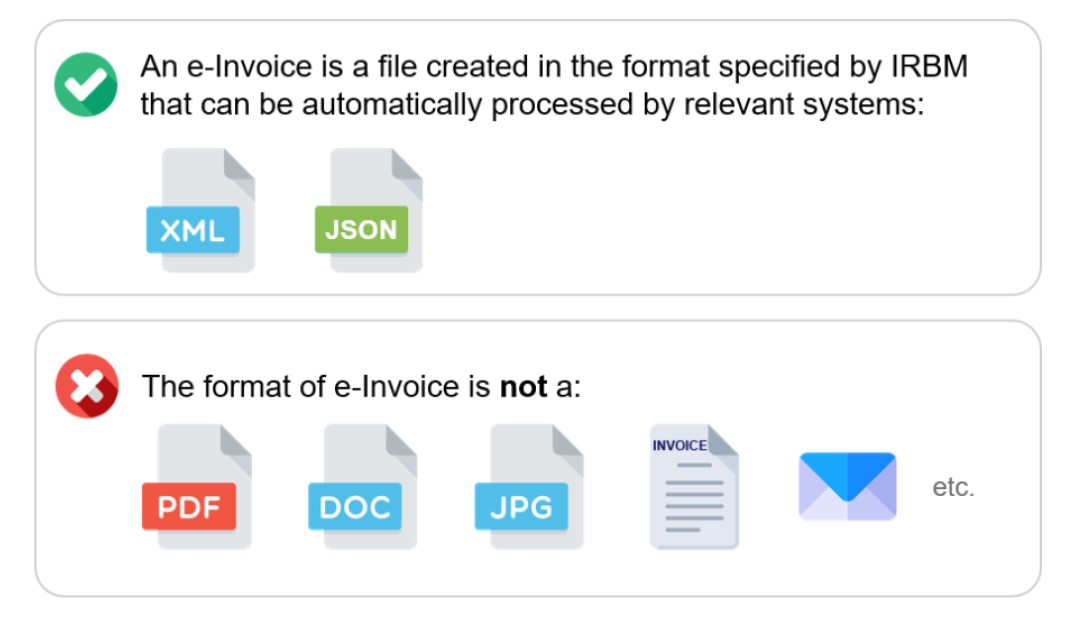
5. What formats are accepted for e-Invoices in Malaysia?
The IRBM accepts e-Invoices in XML or JSON formats, adhering to the Universal Business Language (UBL) 2.1 standard.
6. How will e-Invoicing affect cross-border transactions?
While e-Invoicing primarily targets domestic transactions, businesses engaged in international trade should stay informed about any additional requirements or guidelines issued by the IRBM.
7. What support is available for businesses transitioning to e-Invoicing?
The IRBM provides guidelines, FAQs, and a Software Development Kit (SDK) to assist businesses. Additionally, consulting with tax professionals or e-Invoicing solution providers like BDO can facilitate a smoother transition for your business.
8. What are the consequences of non-compliance with e-Invoicing regulations?
Non-compliance may result in penalties, fines, or other enforcement actions by the IRBM. It's crucial for businesses to adhere to the implementation timelines and requirements to avoid such consequences.
9. How long should I keep e-Invoices for tax purposes?
The IRBM typically requires businesses to retain financial records, including invoices, for a specified period (usually 7 years) for tax audits and compliance purposes.
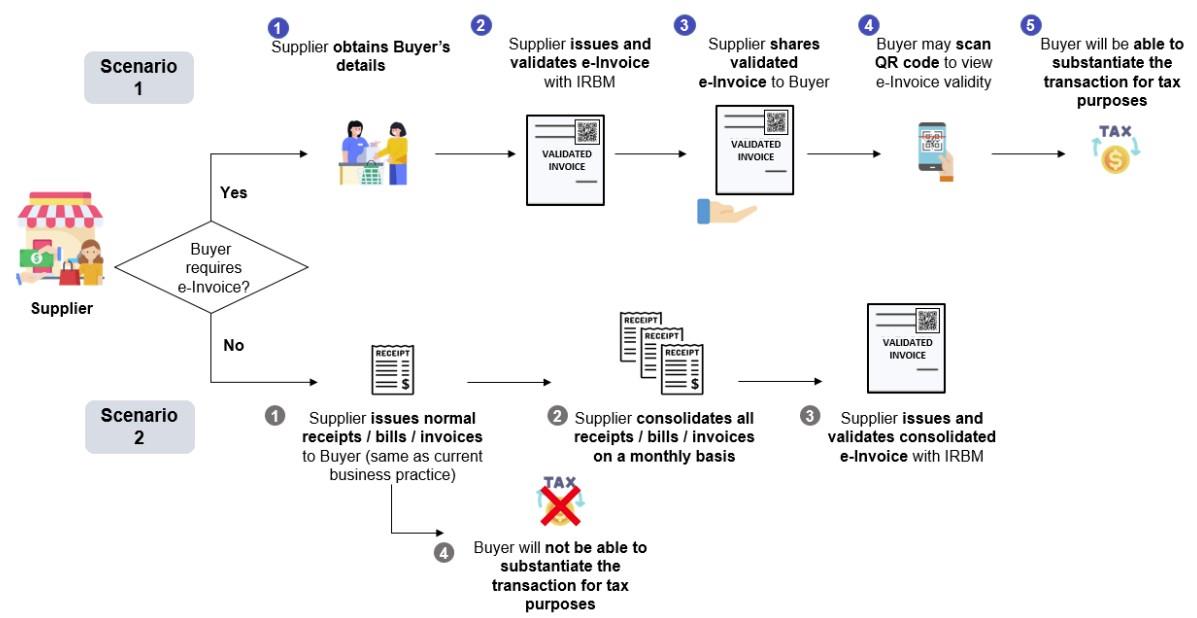
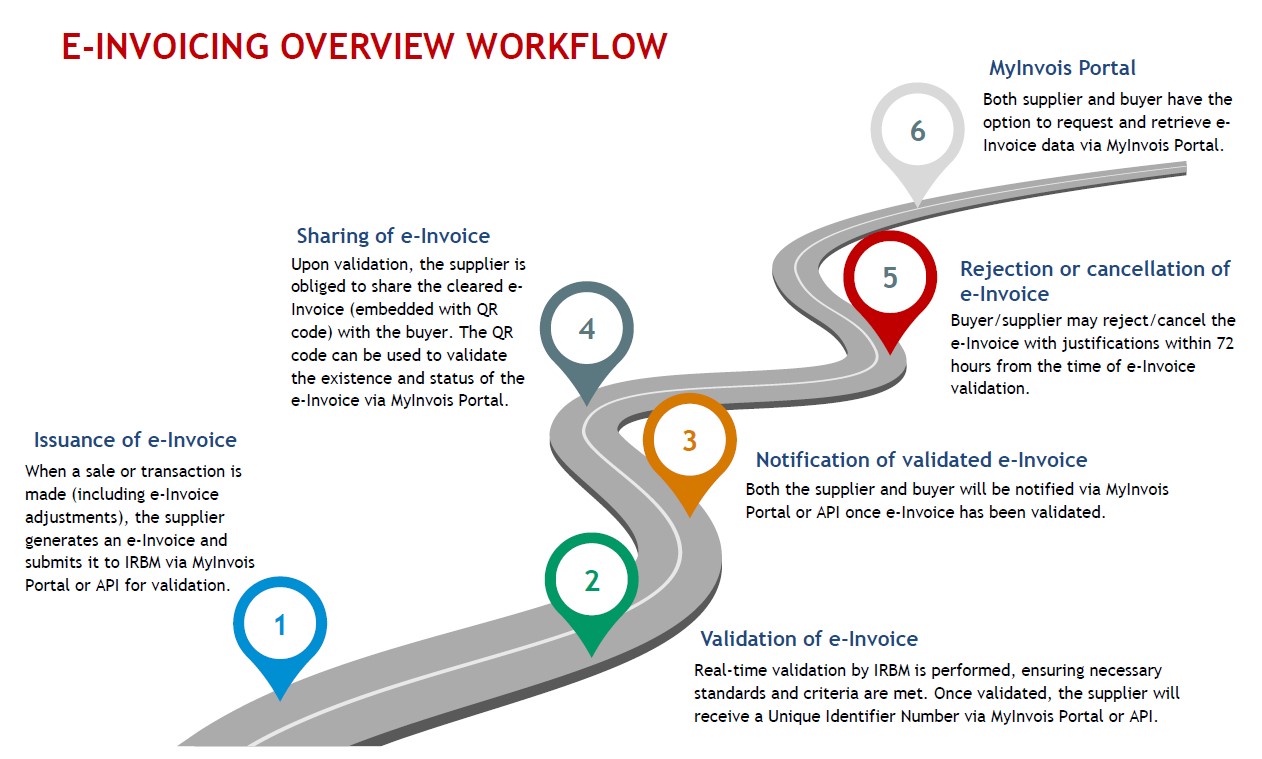
10. Can I submit e-Invoices in bulk, or do I need to upload each invoice individually?
The MyInvois system and most e-Invoicing platforms allow for bulk submissions, which can save time for businesses handling high volumes of transactions. See how our e-Invoice Middleware can help.
11. How does e-Invoicing benefit SMEs specifically?
For SMEs, e-Invoicing can streamline invoicing processes, reduce administrative costs, and ensure compliance with tax regulations. It also levels the playing field by allowing smaller businesses to operate with the same efficiency as larger companies.
12. How does e-Invoicing align with environmental sustainability goals?
e-Invoicing reduces the need for paper invoices, lowering your business's paper consumption and contributing to environmental sustainability. It also cuts down on storage requirements, reducing physical waste and promoting a greener business operation.
.jpg)
.jpg)